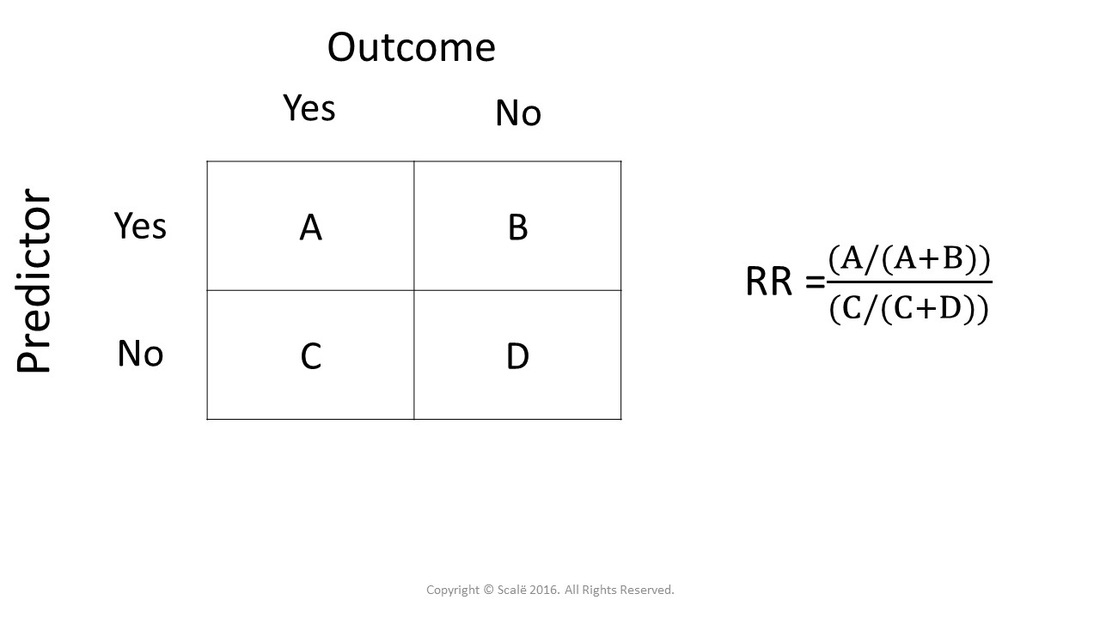
In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − pBased on this information, the odds ratio estimate 24 45 = = v u ˆOR = 1, indicating that low fruit/veggie "exposure" was associated with an % increase in risk The 95% confidence interval for the odd ratio parameter is calculated The ln(OR^) = and 24 1 45 1 1 1 = = u v SE ln ˆOR = Therefore, the 95% confidence Thus, if the confidence interval includes 1 (eg, 001, 2, 099, 101, or 099, 100 all include one in the confidence interval), then the expected true population odds ratio may be above or below 1, so it is uncertain whether the exposure increases or decreases the odds of the event happening with our specified level of confidence

Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk
What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk-The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol The pvalue is 0007 This is same as I saw in the research paper And the Odds Ratio is given as 4 and 95% CI is () I would like to know how to calculate Odds Ratio and 95% Confidence interval for this?




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
Diagnostic odds ratio In medical testing with binary classification, the diagnostic odds ratio ( DOR) is a measure of the effectiveness of a diagnostic test It is defined as the ratio of the odds of the test being positive if the subject has a disease relative to the odds of the test being positive if the subject does not have the disease For pediatric arrest, the risk of survival if intubated during arrest was 411/1135 (36%) vs 460/1135 (41%) if not intubated Let's convert to odds and calculate an OR Intubated 411/ = 411/724 = 057 odds Nonintubated 460/ = 460/675 = 068 odds The most active quartile of women had a similar risk of breast cancer as the least active (odds ratio OR, 104;
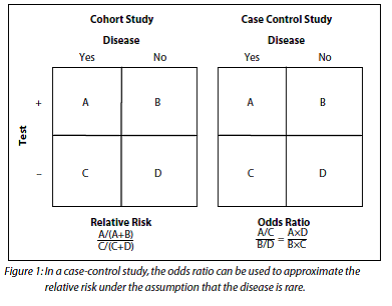
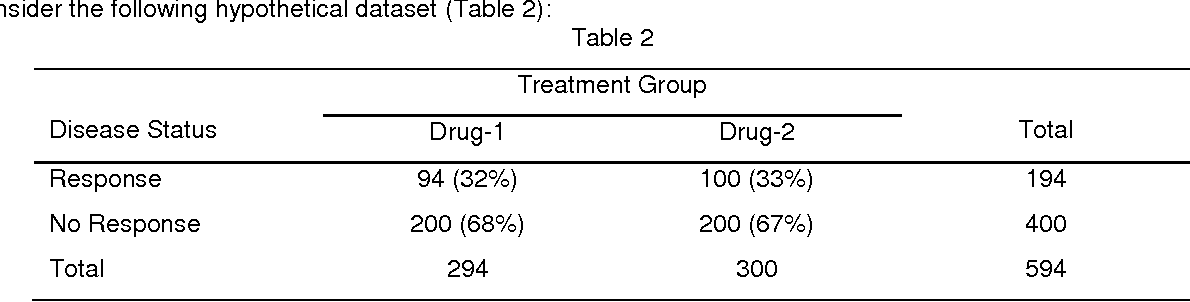
95% confidence interval (CI), 073–148)Approximation to the risk ratio since, in this case, 1−p1≈1−p2, so that ψ ≈ =φ − − = 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 p p p p p p Confidence Intervals for the Odds Ratio Many methods have been devised for computing confidence intervals for the odds ratio of two proportions 2 2 1 1 1 1 p p p p − − ψ= Eight of these methods are available in the Confidence Intervals for Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios You are already familiar with risk ratios and odds ratios Risk ratio RR = CI e /CI u where CI e =cumulative incidence in exposed (index) group and CI u = cumulative incidence in the unexposed (reference) group Odds ratio OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in unexposed) Both RR and OR are estimates from samples, and they are continuous measures
Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) Later in the chapter we will cover how confidence intervals are applied to RR & OR ERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi for pointing this typo out in a youtube comment!The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a studyOdds Ratio \u0026 Relative Risk Calculation \u0026 Definition, Probability \u0026 Odds Binary Logisitic Regression in SPSS with Two Dichotomous Predictor VariablesRelative Risk vs Odds ratio Confidence Interval Interpretation 95% Confidence Interval 90% 99% STATA Tutorials Binary Logistic Regression
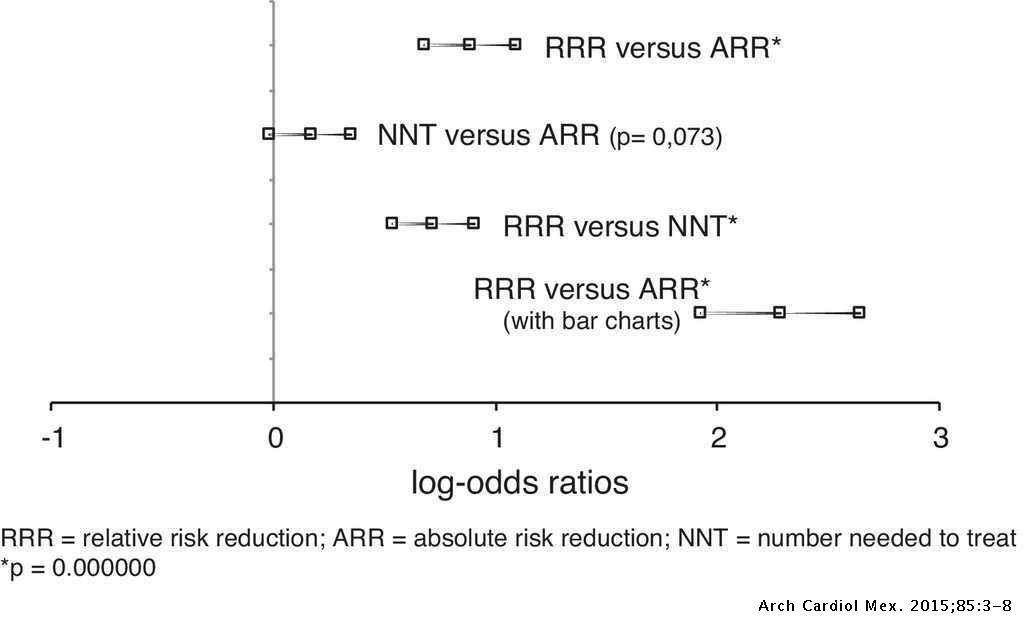



Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
Importance of 95% Confidence interval with odds ratios The 95% confidence interval is perhaps more important than the p value in interpreting the statistical significance of odds ratios Simply put, it is an expression of the spread of the odds ratioThe odds ratio can be confused with relative risk As stated above, the odds ratio is a ratio of 2 odds As odds of an event are always positive, the odds ratio is always positive and ranges from zero to very large The relative risk is a ratio of probabilities of the event occurring in all exposed individuals versus the event occurring in all nonexposed individuals B Confidence Intervals for the Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) The risk difference quantifies the absolute difference in risk or prevalence, whereas the relative risk is, as the name indicates, a relative measure Both measures are useful, but they give different perspectives on the information A cumulative incidence is a proportion that provides a measure of risk, and a relative risk (or risk ratio) is computed by taking the ratio



Marg Innovera




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
A smaller proportion of the probiotic group developed diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use compared with the placebo group (7 (12%) v 19 (34%); Thus, the 95% CI is the interval of values in which the true risk ratio is likely to lie with a probability of 95% To be statistically significant with a P They shouldn't be because they're actually interpreted differently So it's important to keep them separate and to be precise in the language you use The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities




Distribution Of Relative Risk Among Scenarios For Which The Calculated Download Scientific Diagram



Confidence Interval Interpretation Stomp On Step1
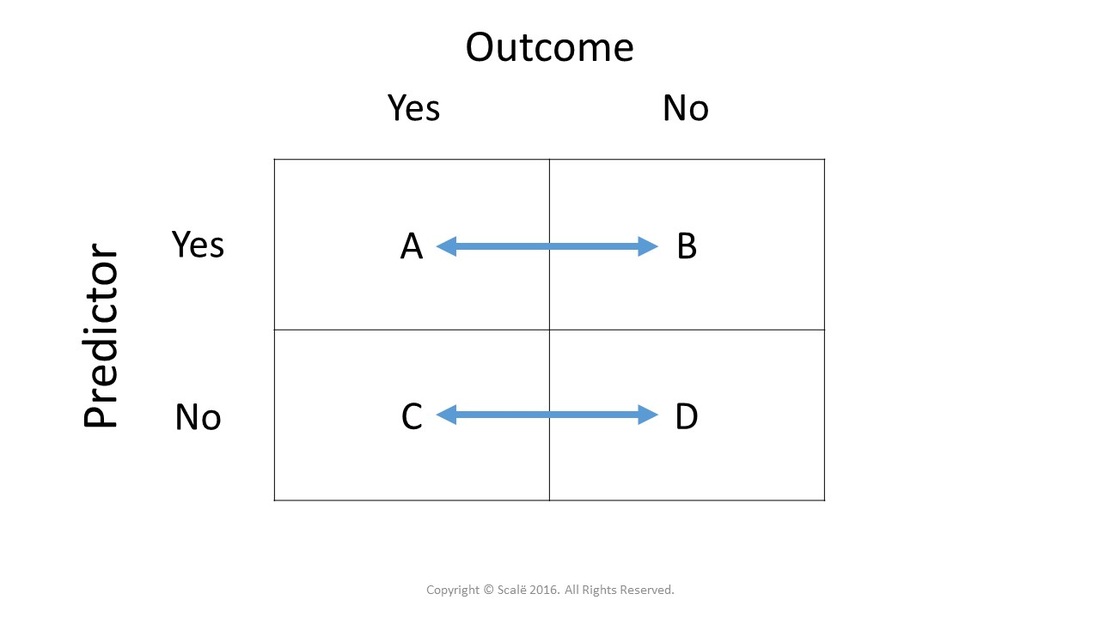
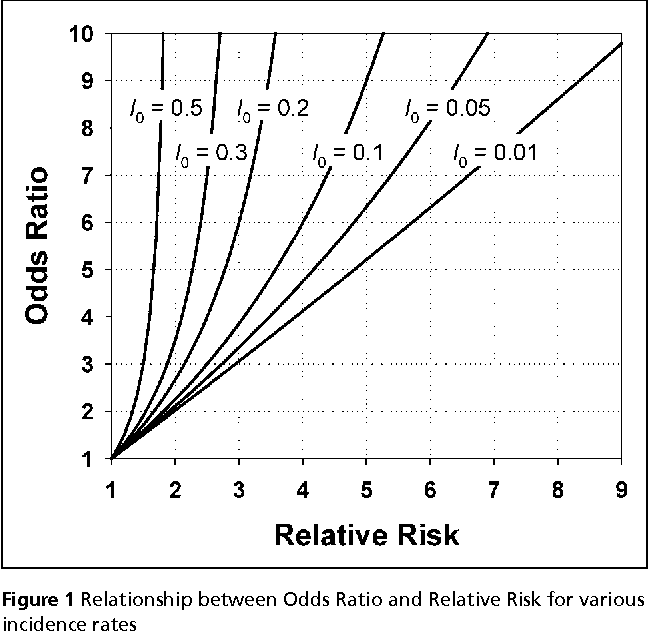
Risk Ratio φ=P 1 / P 2 Odds Ratio 2 1 O O ψ= Although these three parameters are (non linear) functions of each other, the choice of which is to be used should not be taken lightly The associated tests and confidence intervals of each of these parameters can vary widely in power and coverage probability Difference The proportion (risk) difference δ=PAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higher INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated




Literature Search



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age And With Selected Conditions Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd
The concrete problem is that I am refereeing a paper where a confidence interval is presented for the risk ratio and I do not find it credible I show below my attempts to do this in R The example is slightly changed from the authors' I can obtain a confidence interval for the odds ratio from fishertest of course === fishertest example === > outcome < matrix(c(500, 0, 500,The risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RR Having calculated our estimate of effect, we would like a confidence interval for it Ratios are rather difficult things to deal with statistically Because risk ratio is a ratio, it has a very awkward distribution Furthermore, it is shown that different measures result in different impressions Conclusion It is recommended that researchers report both a relative and an absolute measure and present these with appropriate confidence intervals Keywords odds ratio, risk reduction, number needed to treat, medical decision making




There Are Ten Important Calculations In Epidemiology Odds Ratio Prevalence Relative Risk Incidence Control Event Health Disease Disease Diagnostic Testing




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
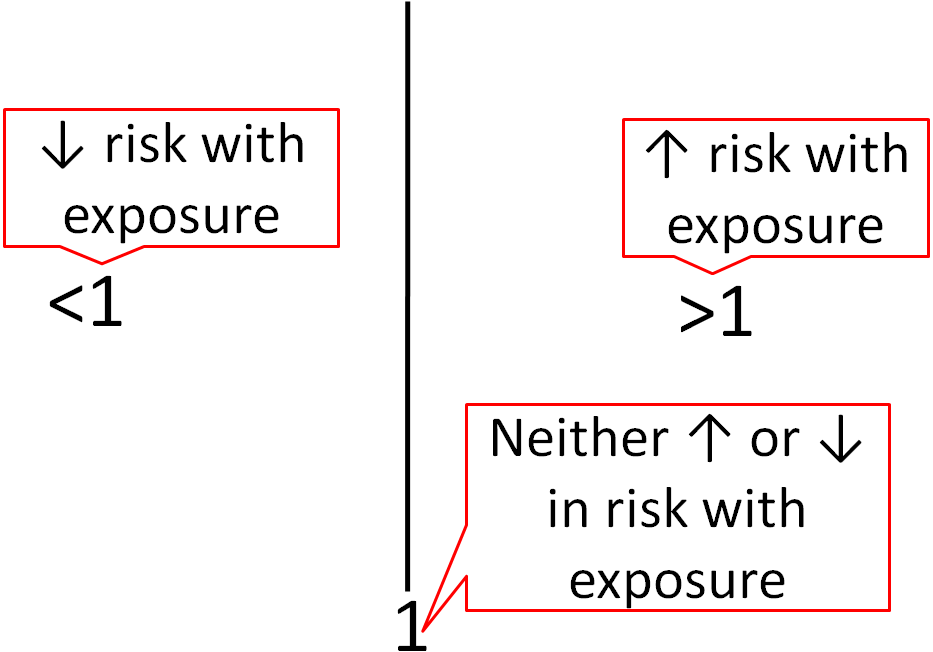
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical I am conducting a metaanalysis and have one study which reports relative risks, and several studies reporting odds ratios I would like to convert the relative risks to odds ratios and obtain corresponding confidence intervals and standard errors I have data on the prevalence of the outcome in the control group, the relative risk and 95% CIsThe relative risk is the ratio of event probabilities at two levels of a variable or two settings of the predictors in a model Estimation is shown using PROC FREQ, a nonlinear estimate in a logistic model, a loglinked binomial model, and a Poisson approach with GEE estimation (Zou, 04)




Test Of Association Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Download Table




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
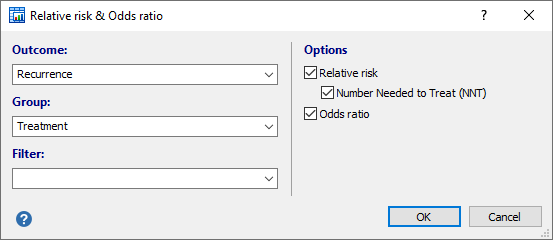
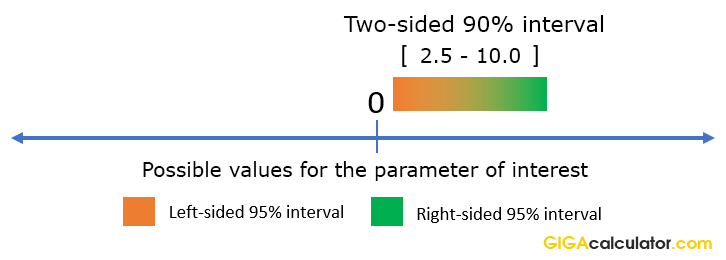
Use the confidence interval to assess the estimate of the odds ratio For example, with a 95% confidence level, you can be 95% confident that the confidence interval contains the value of the odds ratio for the population The confidence interval helps youConfidence Interval for 2 by 2 Odds Menu location Analysis_Exact_Odds Ratio CI Odds = probability / (1 probability) therefore odds can take on any value between 0 and infinity whereas probability may vary only between 0 and 1 Odds and log odds are therefore better suited than probability to some types of calculationRelative Risk Calculator Use this relative risk calculator to easily calculate relative risk (risk ratio), confidence intervals and pvalues for relative risk between an exposed an control group One and twosided intervals are supported for both the risk ratio and the Number Needed to Treat (NNT) for harm or benefit



Support Sas Com Resources Papers Proceedings11 345 11 Pdf




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
Relative risk 036, 95% confidence interval 017 to 079) When adjusted using logistic regression to control for other factors, the effects of the probiotic drink in reducing antibiotic associated The odds ratio is reported as 1 with a confidence interval of (144, 234) Like we did with relative risk, we could look at the lower boundary and make a statement such as "the odds of MI are at least 44% higher for subjects taking placebo than for subjects taking aspirin" Or we might say "the estimated odds of MI were % higher for the placebo group" You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk The study reports that patients with a prolonged electrocardiographic QTc interval were more likely to die within 90 days compared with patients without a prolonged interval (relative risk RR=25;



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
Reporting Odds Ratio The odds ratio comparing death rates after the standard treatment to the new treatment was OR 3 suggesting that those on the control treatment are more likely to die As with the relative risk, the odds ratio is said to be significant if the confidence interval95% confidence interval CI 1541) Having a confidence interval between 15 and 41 for the risk ratio indicates that patients with a prolonged QTc interval were 1541 times more likely to die in 90 days than those without a prolonged QTc intervalA) The Odds Ratio and the corresponding 100(1α)% confidence interval b) The Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) and the corresponding 100(1α)% confidence interval c) The Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) and the corresponding 100(1α)% confidence interval d) The Number Needed to Treat (NNT) and the corresponding 100(1α)% confidence interval




Evidence Of Safety Pooled Relative Risk Rr Or Odds Ratio Or And Download Table



Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models
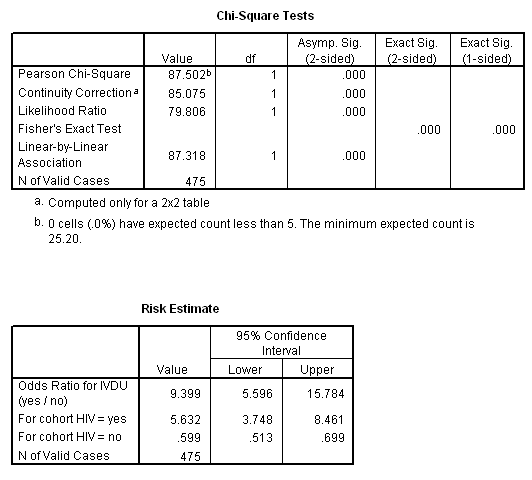
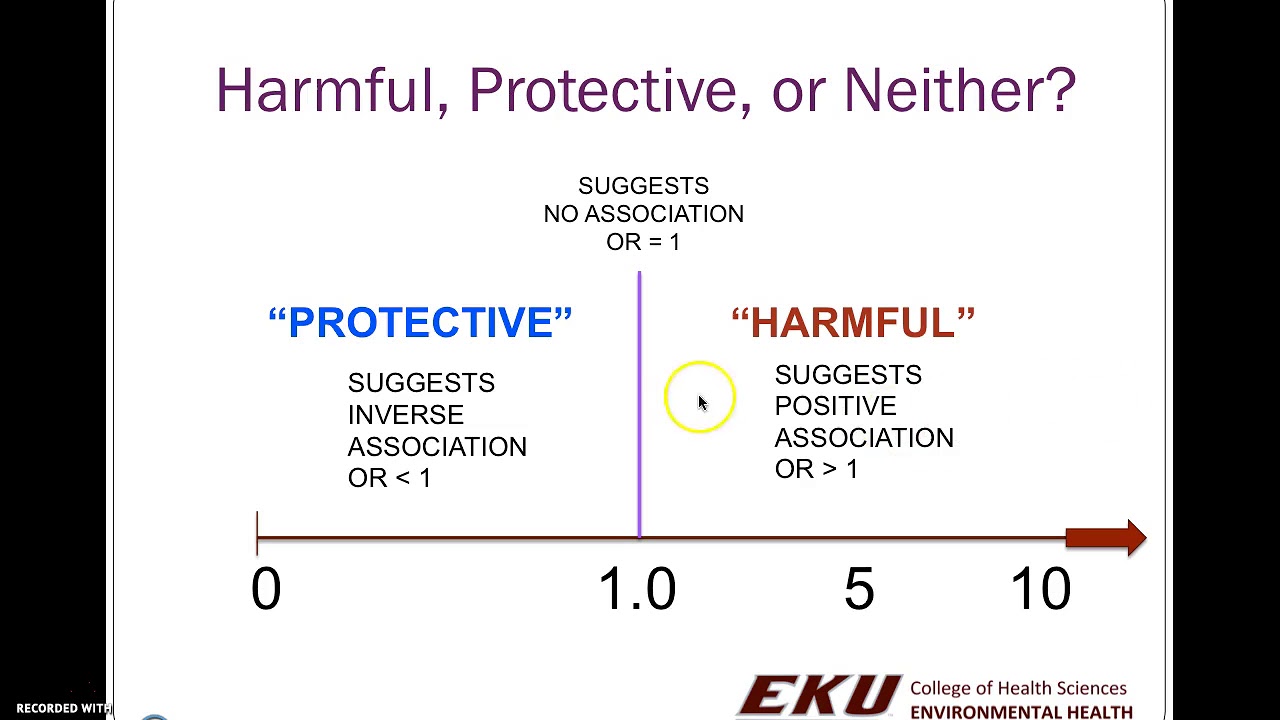
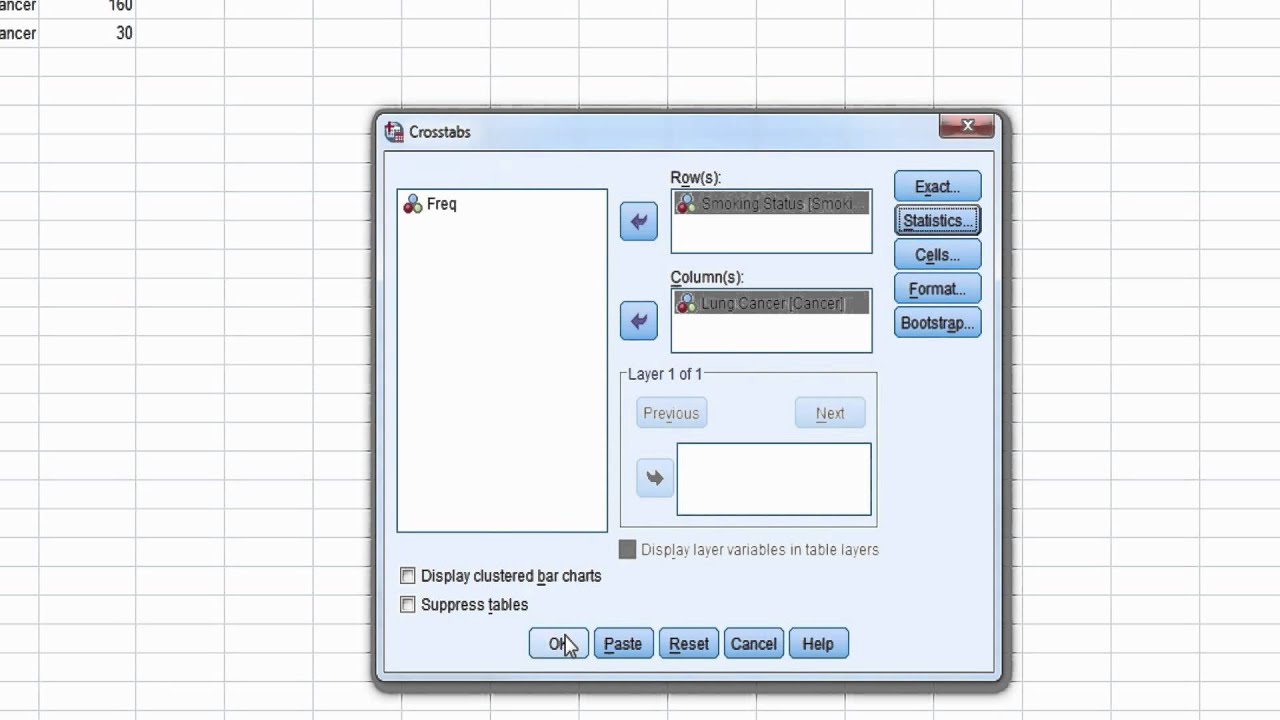
Are there any functions?In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Odds ratio and relative risk for obtaining the following Risk Estimate table Chisquare test is one of the options too Value Figure (a) SPSS Data Editor Figure (b) Weight Cases Figure (c) Weight Cases Confidence interval for odds ratio Odds ratio of having disease for sector 1 vs sector 2 SECTOR * DISEASE Crosstabulation Count 22 95 117



1 Calculate The Odds Ratio The 95 Confidence Chegg Com




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
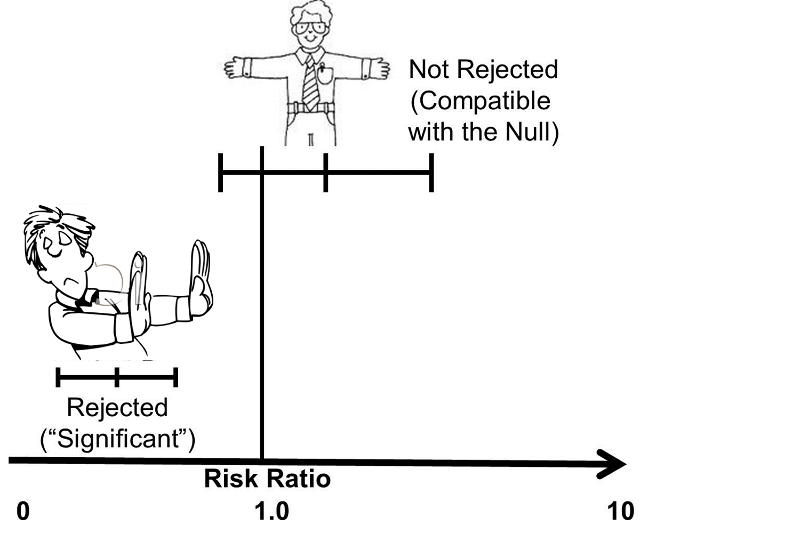
Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeableInterpreting confidence intervals for the odds ratio Interpreting confidence intervals for the odds ratio216 Confidence intervals should be reported;




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram



Question 31 True Or False Using A 95 Confidence Chegg Com
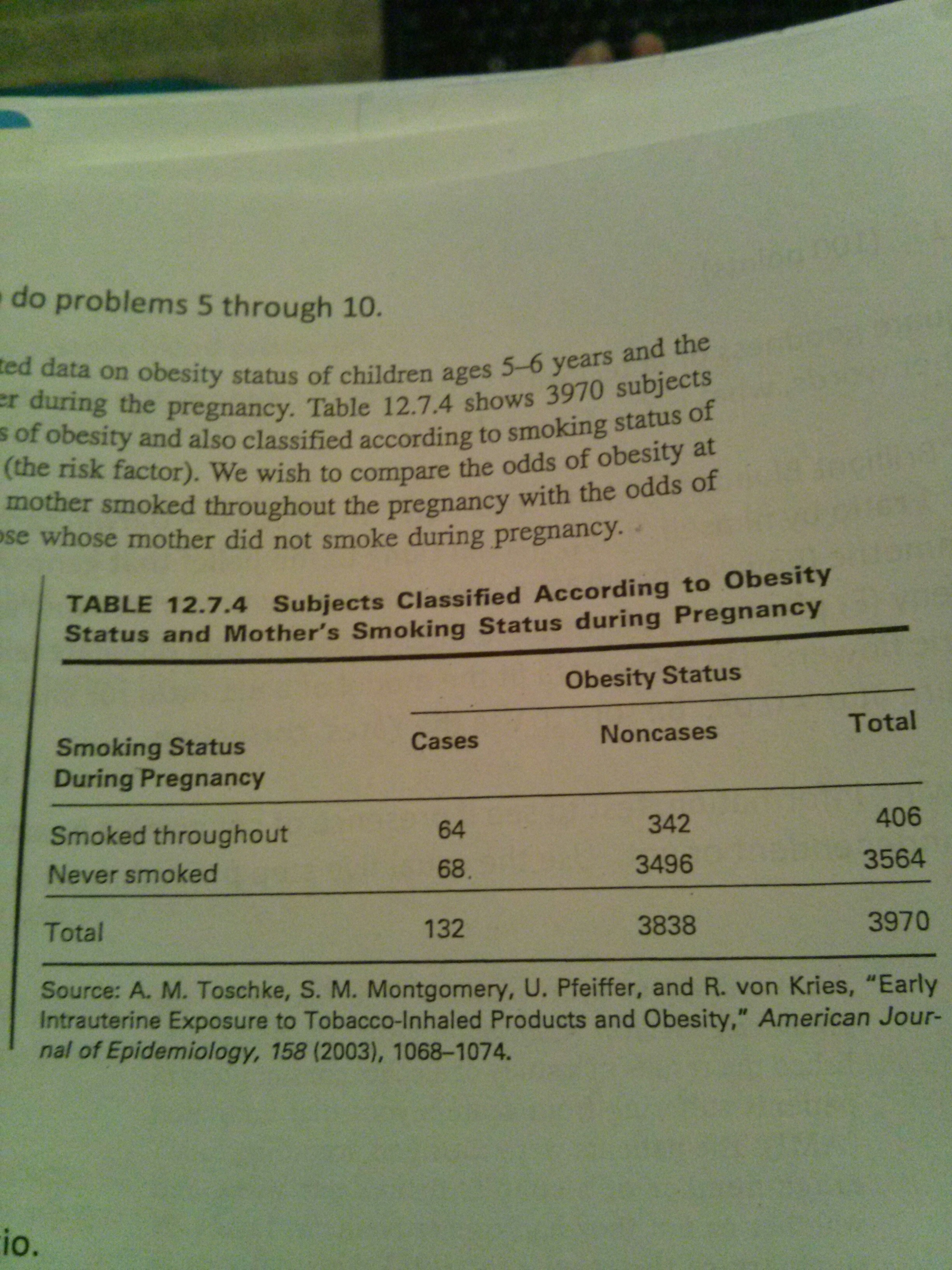
Agresti & Min (01) , (02) look at smallsample confidence intervals for the difference between proportions, and for the relative risk and odds ratio Agresti & Caffo (00) propose a simple interval for the difference between proportionsCan anyone please tell me how can I calculate this in R? In our example, the odds ratio of treatment to control group would be 35 (15 divided by 043) Risk and relative risk Risk, as opposed to odds, is calculated as the number of patients in the group who achieve the stated end point divided by the total number of patients in the group Risk ratio or relative risk is a ratio of two "risks"




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
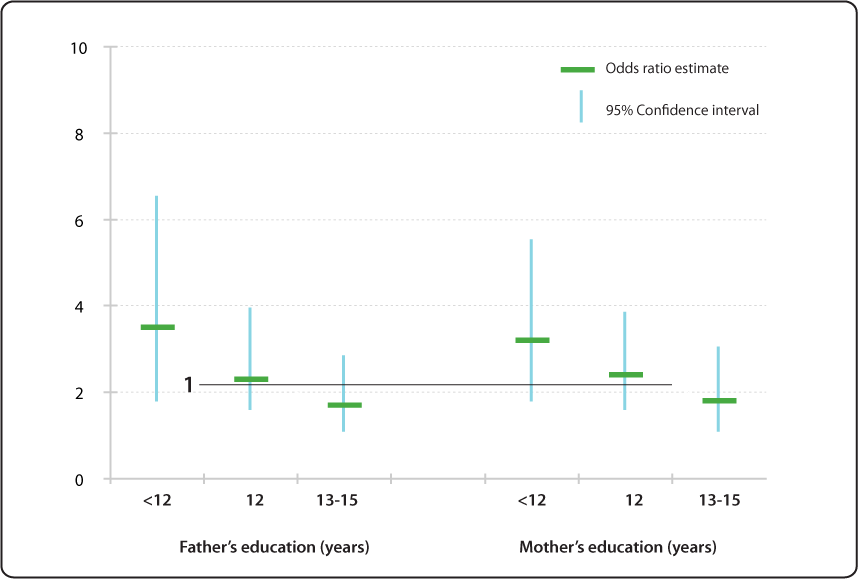



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals Of Children Having Specific Language Impairment Sli By Parent S Level Of Education Reference College Graduate Or More Education 16 Years Nidcd
Biometrics 71, 985–995 DOI /biom December 15 Exact Confidence Intervals for the Relative Risk and the Odds Ratio Weizhen Wang1,2,* and Guogen Shan3 1College of Applied Sciences, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing , P R China 2Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, USA 3Department of Environmental and In the above example, after the odds ratio is corrected (where OR=327 and P 0 =024), the risk ratio becomes 212 (95% confidence interval, ), ie, very low birthweight neonates in Hospital A had twice the risk of neonatal death than those in Hospital BAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk Wikipedia
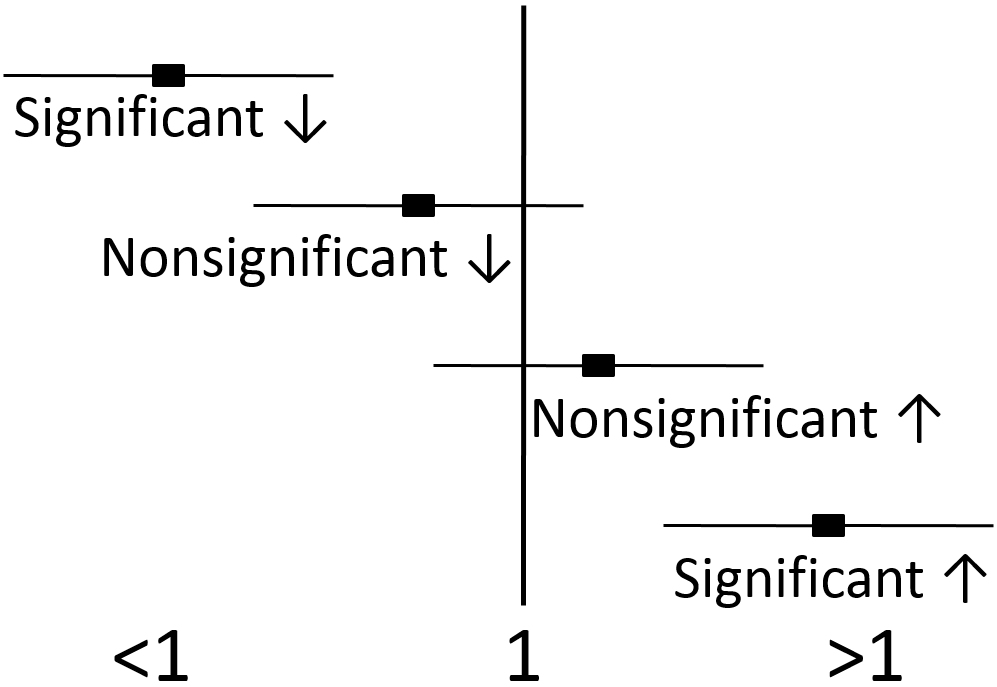
Details This is a basic introduction to interpreting odds ratios, confidence intervals and pvalues and should help healthcare students begin to make sense of published research, which can initially be a daunting prospect The blog features a 'concept check' question as each new element isPopulation attributable risk is presented as a percentage with a confidence interval when the odds ratio is greater than or equal to one (Sahai and Kurshid, 1996) Technical validation A confidence interval (CI) for the odds ratio is calculated using an exact conditional likelihood method ( Martin and Austin, 1991 )If the confidence interval does not cross the line of no difference than the observed difference is statistically significant, because you know it is highly unlikely that the two groups are the same For both relative risk (RR) and odds ratio (OR), the "line of no difference" is 1 So an RR or OR of 1 means there is no difference between




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Document



1



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Of Risk Of Asthma The Pooled Download Scientific Diagram




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Www Jstor Org Stable



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



1 5 Nutrition Research Statistics Nutrition Flexbook




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Hypothesis Testing Objectives N Students Should Be Able



1




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




The Relative Risk Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Comparing Download Scientific Diagram




Statistical Significance Using Confidence Intervals Dr Shaik Shaffi




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Can Tax Deadlines Cause Fatal Mistakes Chance




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Gap Toolkit 5 Training In Basic Drug Abuse



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




When No Overlapping Of The Confidence Interval 0 975 To 10 901 And P 0 055 Odds Ratio 3 2 Is It Significant Or Not



Http Www Wright Edu Weizhen Wang Paper 36 15biometrics Wang Shan Pdf



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Testing Of Hypothesis Homework Help1



Confidence Intervals And P Values



Relative Risk Wikipedia




1 Hypothesis Testing 3 1 1 Hypothesis Test For Mean



Epidemiological Measures




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Volunteer Heart Org Apps Pico Presentation library Understanding forest plots Understanding forest plots Pdf




Relative Risks Odds Ratios With 95 Confidence Intervals Ci Of Rf Download Table




Odds Ratio Article




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Relative Risk Odds Ratio Estimate With 95 Confidence Intervals For People To 66 Years Of Age With Current Medication Use Ever Having Voice Problems Or Disorders Nidcd




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Why The P Value Culture Is Bad And Confidence Intervals A Better Alternative Sciencedirect
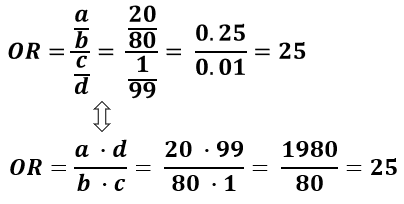



Odds Ratio Calculator Calculate Odds Ratio Confidence Intervals P Values For Odds Ratios




Confidence Intervals And P Values



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Relative Risks Odds Ratio Crude Adjusted 95 Confidence Interval P Download Table




Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Interval Youtube




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance



1 5 Nutrition Research Statistics Nutrition Flexbook




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Confidence Intervals And P Values



Spss Video 10 Obtaining Odds Ratio Relative Risk In Spss Youtube



Http People Stat Sc Edu Hansont Stat5 Lecture19 Pdf



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Pdf Calculation Of Confidence Intervals For Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Using Statxact Semantic Scholar




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



2 Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Youtube



Odds Ratio Calculator Calculate Odds Ratio Confidence Intervals P Values For Odds Ratios



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿